What Is Egg Quality, and How Can It Be Measured in the IVF Lab?
In the context of in vitro fertilization (IVF), egg quality refers to the genetic and developmental integrity of a woman's oocytes (eggs). High-quality eggs are chromosomally normal (euploid), containing 23 chromosomes. When fertilized, they form embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, increasing the likelihood of successful implantation and a healthy pregnancy.
Assessing Egg Quality in the IVF Laboratory
Directly testing the quality of individual eggs before fertilization is challenging. However, several methods are employed to evaluate and select the most viable eggs for IVF procedures:
Morphological Evaluation: Embryologists examine the physical characteristics of oocytes under a microscope, assessing factors such as:
Cytoplasm: A clear, homogenous cytoplasm is indicative of a healthy egg.
Zona Pellucida: The outer membrane should be uniform in thickness.
Perivitelline Space: The area between the egg's membrane and the zona pellucida should be free of debris.
Polar Body: The presence and position of the polar body can provide insights into the egg's maturity.
Oocyte Size Measurement: Larger oocytes are generally considered of higher quality, as they may contain more cytoplasm and better organelle distribution, potentially leading to improved embryo development.
Perivitelline Space Analysis: Evaluating the size and content of the perivitelline space helps in assessing oocyte quality. A thinner perivitelline space devoid of granulation is preferable, though some granules may be normal.
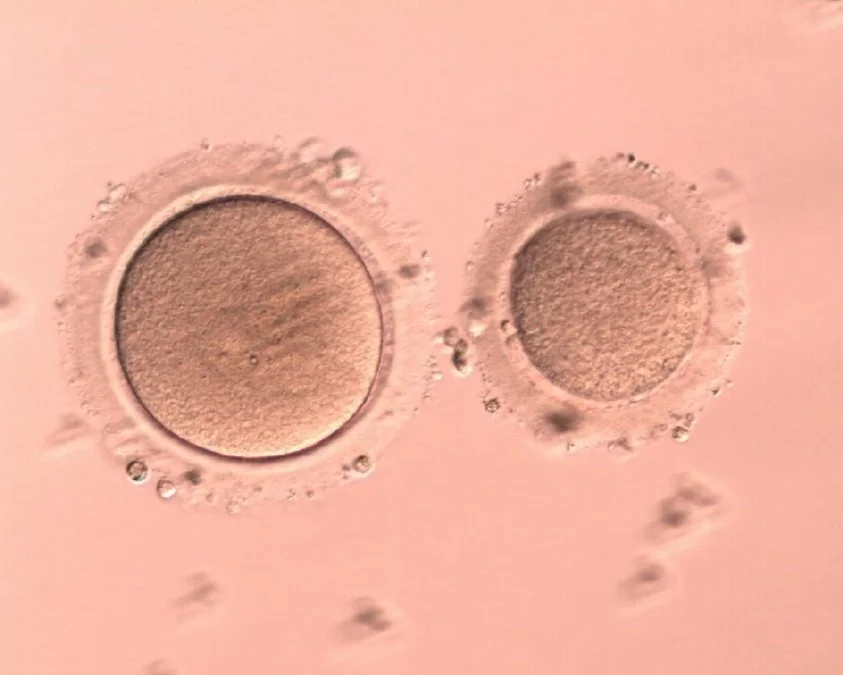
Looking at the image below, you perform the morphological evaluation yourself. Regardless of how “good” this evaluation may be, it won’t actually determine the true health of an egg.
Here is an example of a giant egg and a regular sized egg.
Limitations and Considerations
While these laboratory assessments provide valuable information, they do not guarantee the chromosomal normalcy of an egg. The only definitive method to determine chromosomal integrity is through fertilization and subsequent genetic testing of the resulting embryo. It's important to note that as women age, the proportion of chromosomally normal eggs decreases, which can impact IVF success rates.
Advancements in Egg Quality Assessment
Researchers are continually exploring new techniques to improve the assessment of egg quality. For instance, studies have investigated the use of zona pellucida birefringence imaging to predict embryo development potential. However, more research is needed to standardize these methods and confirm their effectiveness.
Many studies are being conducted on egg quality assessment, and some have even commercialized their success through AI imaging. In the meantime, regular labs must continue relying on physical evaluations until new research becomes clinically available.
Well, what about lifestyle changes or supplements? Harvard seems to think so, check out their article from 2020 on fertility and diet!
Conclusion
Assessing egg quality in the IVF lab involves a combination of morphological evaluations and measurements to select the most viable oocytes for fertilization. While these methods aid in identifying eggs with the best potential, they cannot definitively determine chromosomal normalcy. Ongoing research aims to refine these assessment techniques, enhancing the success rates of IVF treatments.
“Haha, you think anything is stopping me from fertilizing that egg?”